INDEX
What is aiESG?
Products and Servicesindicates certainty, emphasis, etc.All supply chainback in time.
ESG Assessment ServicesIt is!
Hello, we are an ESG Tech startup from Kyushu University! We are an ESG Tech startup from Kyushu University!
In this column, we will introduce global ESG trends, our services, and case studies for those who are "interested in aiESG," "want to conduct ESG analysis but do not know what to do," or "what is ESG in the first place? This column introduces global trends in ESG, our services, and case studies. We will also regularly introduce the voices of our staff members who work at our company.
In this first column, I will give you some background on how we started our service.
ESG Management Now and What is Required
Less than 20 years after the United Nations advocated in 2006 for institutional investors to have an "ESG" (environmental, social, and corporate governance) perspective, the importance of ESG initiatives in companies is increasing worldwide. Investments that investors make with corporate sustainability in mind are referred to as sustainable or ESG investments. Sustainable investing is a form of investment that includes ESG investing and is based on the assumption that a company or industry is sustainable.ESG investing is a form of investment in which investors are concerned about corporate social responsibility and are interested in environmental (Environment) and corporate initiatives on social issues (sadistsocial), legal compliance (g(overence) and other governance transparency in investing.
GSIA (Global Sustainable Investment Alliance), an organization that promotes sustainable investment through a collaboration of ESG research organizations in various countries.1)According to the "Sustainable Investments for ESG Considerations", the total global value (in 2020) of sustainable investments that take ESG into account is $35.3 trillion (approximately 4,600 trillion yen). Furthermore, with growth rates of around 10% annually over the past few years, it is expected that the importance of addressing ESG issues will continue to grow in the future.
The $35.3 trillion represents 35.91 TP3T of the $98.4 trillion in total assets under management of the institutional investors surveyed. This means that more than 30% of all assets under management fall under ESG investments as defined by the GSIA, and ESG considerations have become an important factor in investors' decisions. Against this backdrop, an increasing number of companies are taking these considerations into account in their management, but there are also cases of "greenwashing" (pretending that a company is taking environmentally friendly actions when in fact it is not), and this is being viewed as problematic. It is not easy to determine on what basis a company claims to be "environmentally conscious" or "respecting the human rights of those involved in the supply chain (supply chain). ESG data that can be objectively demonstrated to investors, business partners, and consumers are now in demand.
Growing interest in human rights items throughout the supply chain
Among ESG initiatives, human rights issues through the supply chain have received particular emphasis in recent years. Figure 1 below shows the change in ESG investments between 2015 and 2021 by world region.
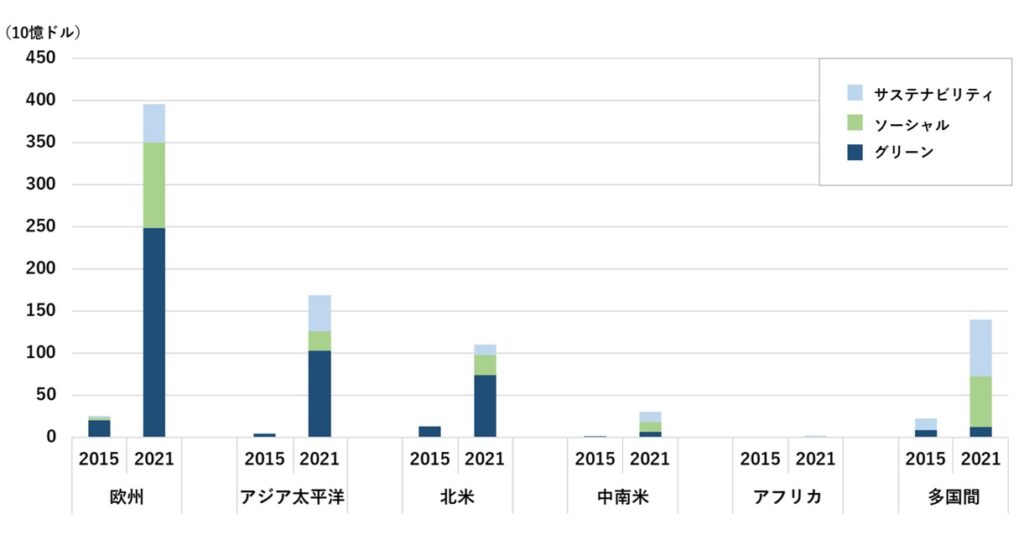
Figure 1: Global ESG Investment Change by Region
Created from Interactive Data Platform (Climate Bonds Initiative)
Green indicates investments in environmental damage prevention, Social indicates investments in human rights risks and community engagement in the supply chain, and Sustainability indicates investments in climate change prevention ESG-focused investments have increased significantly from 2015 to 2021 ESG Investment Value Overall, Europe leads the way, followed by Asia-Pacific and North America. Overall, green investments, which are investments in the environment, account for a large share of ESG investments, but social investments, which are investments in human rights, have increased in recent years.
Thus, while the movement to encourage the development of sustainable supply chains has traditionally focused on the areas of environmental destruction prevention and climate change countermeasures, in recent years there has been an increase in the development of norms related to human rights. For example, in February 2022, the European Commission (EC) will issue a draft directive mandating corporate sustainability and due diligence (ongoing efforts to prevent and remedy adverse human rights and environmental impacts of business activities)2)The "Corporate Social Responsibility" (CRS) is a new initiative by the Ministry of the Environment. Companies are now required to promote sustainable and socially and morally responsible corporate behavior by anticipating and correcting negative impacts of their business activities in all processes of providing products and services.
In Japan, in September 2022, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) will adopt the "United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights" (UNGP).3)and "OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Corporate Behavior."4)Guidelines for Respecting Human Rights in Responsible Supply Chains, etc." based on the5)and encouraging companies to address human rights risks is accelerating (Figure 2). Furthermore, through the development of international standards for sustainable procurement (e.g., ISO 20400) and engagement (proposals to invest in a company that will increase its corporate value) and divestment (investment withdrawal) by ESG investors, the demand for ESG responses throughout the supply chain is further increasing.
Figure 2: Establishment of regulations on human rights-conscious corporate behavior
In order to implement optimal ESG-conscious supplier evaluation and management in the future, it will be necessary to understand ESG risks in more detail and their impact on the company beyond the traditional evaluation of initiatives at the company level, taking into account upstream supply chains at the product and service level. The following is a brief overview of the ESG risk management process.
References
- Global Sustainable Investment Aliance: GLOBAL SUSTAINABLE INVESTMENT REVIEW 2020, https://www.gsi-alliance.org/.
- Japan External Trade Organization (JETRO): European Commission releases draft directive on mandatory human rights and environmental due diligence,https://www.jetro.go.jp/biznews/2022/02/270ab8bbbd9b69d1.html,2022.02.28.
- United Nations Information Center: Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights.https://www.unic.or.jp/texts_audiovisual/resolutions_reports/hr_council/ga_regular_session/3404/,2011.03.21.
- OECD: OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Corporate Behavior,.https://mneguidelines.oecd.org/OECD-Due-Diligence-Guidance-for-RBC-Japanese.pdf, 2018.
- Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry: Guidelines for Respecting Human Rights in Responsible Supply Chains, etc.https://www.meti.go.jp/press/2022/09/20220913003/20220913003-a.pdf,2022.09.















