INDEX
IAF(International Accreditation Forum)/ISO(International Organization for Standardization) made a significant revision in February 2024, supplementing the existing articles of the current ISO management system standard with the addition of "climate change considerations" and "stakeholder engagement". This update is intended to emphasize the importance of consistent implementation across the organization to effectively address climate change.
This paper briefly summarizes the ISO amendments and discusses the actions that Japanese companies should take.
Table of Contents
What is ISO (International Organization for Standardization)?
What is the new ISO Climate Change Amendment?
The purpose of the amendment is to clarify the relevance of climate change to business.
What are the advantages for Japanese companies?
How will you respond to the correction?
summary
What is ISO (International Organization for Standardization)?
It is a worldwide independent organization that develops standards (= ISO standards) to assist companies in improving quality, safety, and operational efficiency. ISO standards are extremely important to companies because they are recognized as benchmarks for streamlining business processes, improving the quality of products and services, and complying with international regulations. Through these standards, companies can demonstrate their commitment to transparency, continuous improvement, and corporate responsibility.
What is the new ISO Climate Change Amendment?
Adopted in September 2021.The London Declarationhas become a key commitment by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to address the global climate change emergency. This declaration mandates that all new and existing ISO standards incorporate climate change considerations.
Directed by ISO members from 165 countries, the aim of the declaration is to ensure that climate change is integrated into international standards, promote sustainable practices throughout industry, and accelerate the transition to net zero emissions.
Changes
The February 2024 ISO modifications are 31 (covered standards), including ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 27001.Table 3.as listed above) to the ISO standard. It requires organizations to assess the relevance of climate change to their operations and to consider expectations from stakeholders.
Table 1: 31 items added and modified to the ISO standards
| Section 4.1, "Climate Change Considerations." | Business organizations "must" decide if climate change is a potential problem for their business operations. |
| Section 4.2, "Stakeholder Involvement." | Engaged stakeholders can impose conditions on the organization about climate change |
The purpose of the ⚫︎ amendment is to clarify the relevance of climate change to business.
This amendment affects a specific standard. The standards covered are the basis for management in all industries. The reason this amendment covers 31 standards is to more broadly integrate climate change into the management system.
We hope that this amendment will not force companies to respond to climate change, but rather provide an opportunity for them to start thinking about the impact of climate change on their business, even if they have ISO certification (e.g. ISO for road safety). We hope that this will be an opportunity for even ISO-certified companies (e.g., ISO for road safety) to start considering climate change.
However, what the amendment calls for is the addition of two small chapters in the report on climate change linkages and stakeholder impacts, which alone will not accomplish all of ESG responsiveness. companies that are serious about ESG responsiveness are the ones that will benefit most from transparency and sustainable projects. can reap the many benefits of promoting
⚫︎ What are the advantages for Japanese companies?
This ISO amendment will bring a number of benefits to corporate management that go beyond mere regulatory compliance. First, integrating climate change responses into business strategies may facilitate access to new contracts and markets. Many global companies and investors place a high value on ESG compliance in the supply chain, and this ISO amendment will help meet those requirements.
However, in order to reap these benefits, companies must go beyond climate change to address ESG as a whole and put specific policies and projects into action. Therefore, it is hoped that the amendment will act as a trigger to ESG compliance.
References:.
The main drivers from the three perspectives of academia, business, and citizenship - Sustainable ESG-oriented supply chains: a strategic imperative for modern business.
How will you respond to the correction?
The said modifications, as mentioned above, encourage a proactive response on the part of the corporate organization. In this regard, it is important to understand and address the issue of climate change in an "integrated" manner rather than segmenting and modifying corporate operations. Based on these considerations, the following responses may be expected (see Figure 1 and Table 2).
Figure 1: Simplified corporate response flowchart
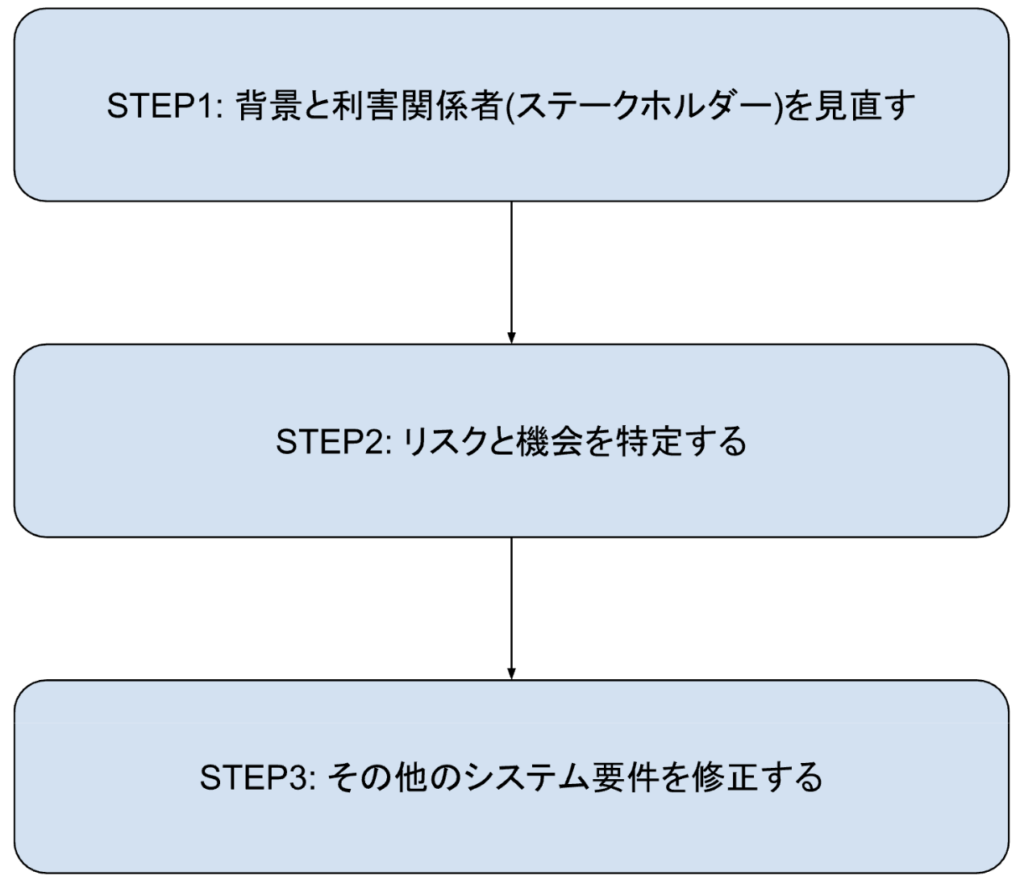
Table 2: Flowchart Explanation
| STEP1: Review background and stakeholders | - Evaluate your organization's goals and how climate change will affect their achievement - Identify stakeholders and understand their climate change expectations - Modify the management system to include climate change if it impacts business operations or stakeholder expectations |
| STEP2: Identify risks and opportunities | - Identify risks (e.g., supply chain, regulatory compliance) and opportunities (e.g., sustainable products, energy efficiency) related to climate change that may affect your organization - Evaluate these risks and opportunities and determine if actions are needed to address them |
| STEP3: Modify other system requirements | - If changes are necessary, update the management system to include Obligation to comply Business Procedures Infrastructure Investment Training Program Internal and external communication on climate change |
summary
The ISO's climate change-aware modifications are a response that will affect many companies. A brief summary of the course of action would be as follows
| Companies "must" determine the impacts of climate change within their business management, and in addition, they must consider how climate change will affect their stakeholders. Climate change decisions, discussions, and any changes in behavior during the review phase should be "documented". Furthermore, it would be "expected" to set targets and management systems to address climate change. |
The entire supply chain analysis is a key document in considering how a company's activities relate to climate change. Quantitative judgments of carbon emissions and labor environment analysis are expected to become the most important criteria for investment decisions and should not be ignored. In addition, as companies become more aware of climate change, they are expected to consider their ESG strategies. To better understand their ESG performance, companies need to understand the overall impact (environmental as well as social) of the supply chain used to manufacture their products.
aiESG provides precise ESG analysis by tracing back upstream the supply chain of a company's product offerings. If you are a company considering a climate change/ESG strategy through this ISO revision and require an analytical response, please contact us.
Contact us:https://aiesg.co.jp/contact/
Table 3: List of ISO standards to be revised (ISOTranslated by aiESG with reference to the material in the "aiESG")
| ISO/IEC 27001:2022 | Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection - Information security management systems - Requirements - Information security management systems - Requirements |
| ISO/IEC 20000- 1:2018 | Information technology - Service management - Part 1: Service management system requirements management system requirements |
| iso/iec 19770- 1:2017 | Information technology - IT asset management - Part 1: IT asset management systems - RequirementsInformation technology - IT asset management - Part 1: IT asset management systems - Requirements |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality management systems - Requirements |
| ISO 50001:2018 | Energy management systems - Requirements with guidance for use |
| ISO 46001:2019 | Water efficiency management systems - Requirements with guidance for use |
| ISO 45001:2018 | Occupational health and safety management systems - Requirements with guidance for use |
| ISO 44001:2017 | Collaborative business relationship management systems - Requirements and framework Requirements and framework |
| ISO 41001:2018 | Facility management - Management systems - Requirements with guidance for use with guidance for use |
| ISO 39001:2012 | Road traffic safety (RTS) management systems - Requirements with guidance for use |
| ISO 37301:2021 | Compliance management systems - Requirements with guidance for use |
| ISO 37101:2016 | Management system for sustainable development - Requirements with guidance for use Sustainable development in communities Management system for sustainable development - Requirements with guidance for use |
| ISO 37001:2016 | Anti-Bribery Management Systems - Requirements with guidance for use |
| ISO 35001:2019 | Biorisk management for laboratories and other related organisations |
| iso 34101-1:2019 | Sustainable and traceable cocoa - Part 1: Requirements for cocoa sustainability management systems sustainability management systems |
| ISO 30401:2018 | Knowledge management systems - RequirementsKnowledge management systems - Requirements |
| ISO 30301:2019 | Information and documentation - Management systems for records - Requirements Information and documentation - Management systems for records - Requirements |
| ISO 29001:2020 | Sector-specific quality management systems - Requirements for product and service supply organizationsPetroleum, petrochemical and natural gas industries - Sector-specific quality management systems - Requirements for product and service supply organizations |
| ISO 28000:2022 | Security and resilience - Security management systems - Requirements Security and resilience - Security management systems - Requirements Security and resilience - Security management systems - Requirements |
| ISO 22301:2019 | Security and resilience - Business continuity management systems - Requirements Security and resilience - Business continuity management systems - Requirements Security and resilience - Business continuity management systems - Requirements |
| ISO 22163:2023 | Railway applications - Railway quality management system - ISO 9001:2015 and specific requirements for application in the railroad sector management system - ISO 9001:2015 and specific requirements for application in the railway sector |
| ISO 22000:2018 | Food safety management systems - Requirements for any organization in the food chain Food safety management systems - Requirements for any organization in the food chain |
| ISO 21401:2018 | Tourism and related services - Sustainability management system for accommodation - Requirements Tourism and related services - Sustainability management system for accommodation - Requirements |
| ISO 21101:2014 | Adventure tourism - Safety management systems - RequirementsAdventure tourism - Safety management systems - Requirements |
| ISO 21001:2018 | Educational organizations - Management systems for educational Educational organizations - Management systems for educational organizations - Requirements with guidance for use |
| ISO 19443:2018 | Quality management systems - Specific requirements for the application of ISO 9001:2015 by organizations in the supply chain of the nuclear energy sector supplying products and services critical to nuclear safety (ITNS) - Specific requirements for the application of ISO 9001:2015 by organizations in the supply chain of the nuclear energy sector supplying Quality management systems Specific requirements for the application of ISO 9001:2015 by organizations in the supply chain of the nuclear energy sector supplying products and services important to nuclear safety (ITNS) |
| ISO 18788:2015 | Management system for private security operations - Requirements with guidance for use |
| iso 16000-40:2019 | Indoor air - Part 40: Indoor air quality management systemIndoor air - Part 40: Indoor air quality management system |
| ISO 15378:2017 | Primary packaging materials for medicinal products - Particular requirements for the application of ISO 9001:2015, with reference to good manufacturing practice (GMP) requirements for the application of ISO 9001:2015, with reference to good manufacturing practice (GMP) |
| ISO 14298:2021 | Graphic technology - Management of security printing processes Graphic technology - Management of security printing processes |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental management systems - Requirements with guidance for use |
*Related Article*.
The main drivers from the three perspectives of academia, business, and citizenship - Sustainable ESG-oriented supply chains: a strategic imperative for modern business.
Part 2: What services does aiESG provide?










