INDEX
Introduction.
This is a commentary article on the paper co-authored by Li Chao, Chief Data Scientist at aiESG, Keeley Alexander Ryuta, Chief Researcher, and Shunsuke Managi, Representative Director.
This article provides an easy-to-understand explanation of the research and the services provided by aiESG. those interested in ESG data analysis and strategy development are encouraged to read to the end.
Title of paper: Forecasts and insights into Japan's fiscal future: Machine learning-based projections of city-level taxpayer numbers and total income from 2020 to 2100 income from 2020 to 2100
DOI (paper link):https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mlwa.2025.100699
Research Points/Summary
This study used machine learning to forecast the number of taxpayers and total income in 1,896 Japanese cities from 2020 to 2100. The model is highly accurate at over 981 TP3T, ensuring the reliability of its long-term projections: by 2100, the number of taxpayers is projected to decrease by 14.521 TP3T, while total income is projected to increase by 5.211 TP3T and average income is projected to increase by 23.071 TP3T. This suggests that the tax base may be maintained under a declining population due to higher labor participation rates. However, rural areas will see serious declines in taxpayer numbers and incomes, and urban areas may also face income stagnation, underscoring the need for regionally tailored policy interventions.
Background and Objectives
Japan faces the combined challenges of a declining birthrate, an aging and rapidly declining population, and a widening gap between urban and rural areas. In particular, the number of taxpayers and total income, which form the financial basis of local governments, will be greatly affected by future demographic changes. In fact, by 2100, Japan's population is projected to decline by more than 30% from 2020 levels, raising concerns about a shrinking labor force and declining local economies.
This study utilized machine learning and step-by-step update techniques to conduct long-term projections of the number of taxpayers and total income in 1,896 cities nationwide. In particular, we focused on the "taxpayer population," which has been insufficiently delineated in conventional population projections, in order to gain a more precise understanding of the economic situation in each region.
analysis
A total of 45 variables were utilized to project the number of taxpayers, including demographics (32 indicators), land use (6 indicators), night light (NTL), and grid population data. The results of the taxpayer projections were further added as a new variable and used to project average income (total income divided by the number of taxpayers).
XGBoost, which enables high-speed and highly accurate forecasts, is used for the machine learning model. The model is continuously updated by incorporating the latest data, and through "incremental updating," high accuracy is maintained even for long-term forecasts up to the year 2100. In addition, a method called "variable importance analysis" was used to numerically indicate which data had the greatest impact on the forecast.
result
The forecasting model showed very high accuracy. The coefficients of determination (R²) for the number of taxpayers and total income reached 99.631 TP3T and 98.831 TP3T, respectively, with mean absolute errors (MAE) of approximately 1,200 for the number of taxpayers and 6.23 billion for the income.
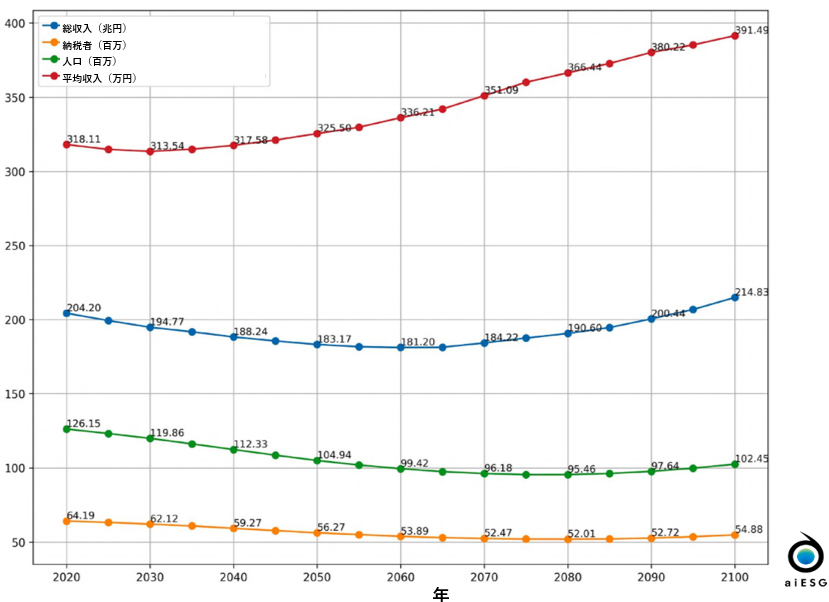
As shown in Figure 1, at the national level, total income is projected to increase by 5.211 TP3T between 2020 and 2100, while the number of taxpayers is projected to decrease by 14.521 TP3T. Average income is projected to increase by 23.071 TP3T and the taxpayer ratio is expected to increase from 50.891 TP3T to 53.561 TP3T.
At the city level, taxpayers and income were concentrated in 2020, but by 2100 taxpayer density had declined nationwide, especially in rural areas. Income was polarized, declining in rural areas while increasing around metropolitan areas. A closer look at metropolitan areas also reveals a reverse urbanization trend, with increases in peri-urban areas and decreases in urban centers.
As for key factors in the projections, the working age population (15-65) and female labor participation rate were shown to have a significant effect on the number of taxpayers, while the number of migrants, the percentage of agricultural land and water areas, and nighttime light were shown to have a significant effect on the average income.
consideration
The results of this study suggest that even as the population continues to decline, the tax base may be maintained to some degree as the percentage of people working rises and average incomes grow. This may be due to advances in technology and changes in employment patterns.
Meanwhile, the gap between urban and rural areas is expected to continue to widen. In urban centers, average incomes are expected to decline due to rising living costs, and "reverse urbanization" will continue as people and incomes are dispersed to the suburbs. Rural areas are facing serious declines in both the number of taxpayers and income due to the outflow of young people and the decline of industry.
These results indicate the need for policy interventions to revitalize local economies and balance economic opportunities. Policy recommendations include promoting labor force participation, investing in local infrastructure, attracting businesses to urban centers, and revitalizing rural areas. In particular, promoting the employment of women and the elderly, developing teleworking infrastructure in remote areas, and adjusting administrative zoning where necessary should be considered.
summary
This study used machine learning to predict with high accuracy the future number of taxpayers and total income for each municipality in Japan. The results revealed that while it is possible to maintain the tax base even under a declining population, it also highlighted the issue of the widening structural disparity between urban and rural areas. Such findings, which take into account demographic and economic structural changes, are important inputs for the ESG assessment provided by aiESG Inc. to quantitatively understand the risks and opportunities of each region, especially from a "social" perspective.
aiESG Inc. provides comprehensive support from organizing and visualizing ESG indicators, including highly accurate forecasting analysis such as in this study, to information disclosure support and practical operations support.
About aIESG's services:https://aiesg.co.jp/service/
















