INDEX
We recently published a commentary report on a Nikkei article published in August of this year on this website.
[Commentary] Nikkei article: aiESG Supply Chain Analysis of "Electric Vehicle (EV) Production, ESG Indicators Deteriorate Due to 'De-China'".
https://aiesg.co.jp/topics/report/2301016_nikkeiev1/
In this report, aiESG will discuss how the U.S. Inflation-Reduction Act (IRA) will affect Japanese manufacturers, based on a proprietary analysis conducted by aiESG.
This additional analysis was also published in the November issue of Nikkei ESG, "Barriers to Entry for ESG Information Set by the EU.
Nikkei ESG published an analysis of EV by aiESG.
https://aiesg.co.jp/topics/news/231017_nikkeiesg/
[Additional analysis
aiESG's independent analysis suggests that ESG indicators for EV in Japan will deteriorate as in the U.S.
Since most Japanese cars are sold in the U.S., the impact of the Inflation-Reduction Act (IRA) may extend to Japanese manufacturers as well. Therefore, apart from the joint analysis with Nikkei Shimbun, "aiESG" also conducted its own ESG assessment of Japanese electric vehicles.
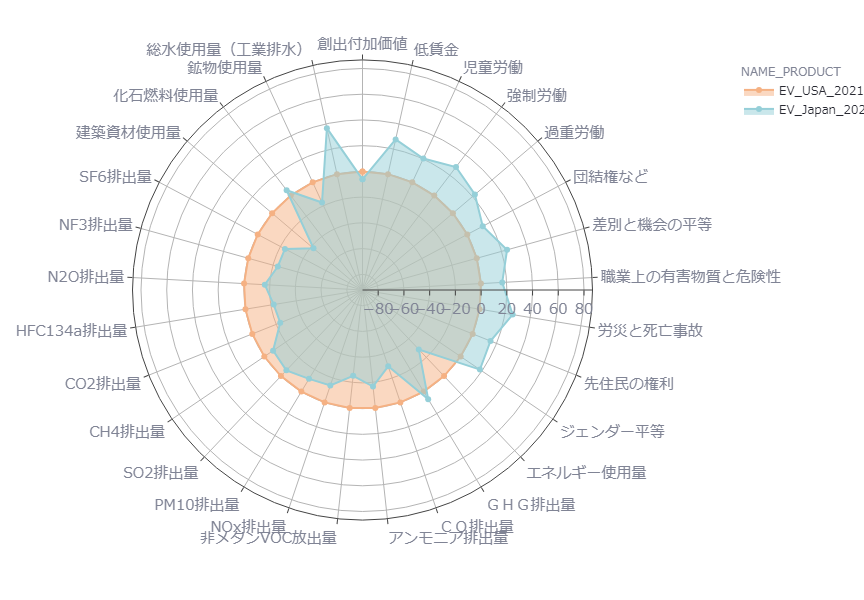
First, a comparison of ESG evaluations of Japanese and U.S. electric vehicles as of 2021 shows that Japanese indicators exceeded U.S. indicators in all categories of human rights risk. Conversely, in the environmental risk category, Japanese indicators fell below those of the U.S. in almost all items. (Figure 1)
The difference in the supply chain, with Japan having a higher proportion of Southeast Asian countries and the U.S. having a higher proportion of Latin American countries, is likely to have influenced the differences in the indicators.
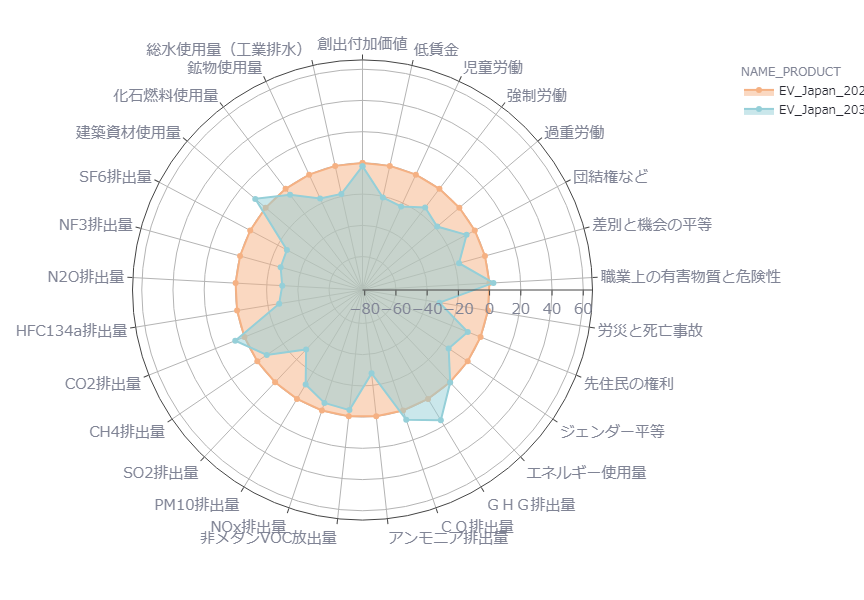
Next, we analyzed changes in ESG ratings for Japanese electric vehicles in 2021 and 2030, and found that, as in the U.S., indicators worsened in 2030 for many items. (Figure 2)
In batteries, which have the greatest impact on the environmental and human rights risks of electric vehicles, the global market is similar, and both Japan and the U.S. have the same major procuring countries, which may explain the similar trends in the indicators in both countries.
Summary
Major ESG challenges lurk in the trend away from EV production in China
Previous ReportIn aiESG, an analysis of aiESG, which can trace supply chains across borders to the end, revealed that both environmental and human rights aspects would deteriorate in ESG assessments if China were excluded from the U.S. electric vehicle supply chain. The shift in the supply of batteries and other components from China to countries surrounding the U.S., such as Mexico, and beyond that to Latin America and Africa, is thought to have an impact on the deterioration of ESG indicators.
In addition, the supply chain for batteries, which have the largest impact on ESG indicators among the various components of electric vehicles, is similar worldwide. For this reason, in this report, aiESG conducted its own analysis of Japanese electric vehicles similar to that of U.S. electric vehicles, and found that ESG indicators may deteriorate in the future for Japanese vehicles as well, just as in the United States.
Through comprehensive ESG assessments of products and services, aiESG supports the development of products and services that conform to ESG perspectives and the formulation of marketing and branding strategies, including the identification of key items to watch from an ESG risk perspective.
If your company is facing challenges in developing ESG-conscious products and services and marketing strategies, please feel free to contact us.
Inquiry about our services:
https://aiesg.co.jp/contact/
*Related Article*.
The front page of the Nihon Keizai Shimbun newspaper featured the results of aiESG's analysis of EV.
https://aiesg.co.jp/topics/news/230815_nikkei/
[Commentary] Nikkei article: aiESG Supply Chain Analysis of "Electric Vehicle (EV) Production, ESG Indicators Deteriorate Due to 'De-China'".
https://aiesg.co.jp/topics/report/2301016_nikkeiev1/
















