INDEX
Introduction.
This article is a commentary on the paper "Human mobility and environmental factors," co-authored by aiESG Chief Data Scientist Li Chao (first author), Chief Researcher Keeley Alexander Ryuta, and Representative Director Shunsuke Managi. environmental factors.
This article provides an easy-to-understand explanation of the research and the services provided by aiESG. those interested in ESG data analysis and strategy development are encouraged to read to the end.
Title of paper: Human mobility and environmental factors
DOI (paper link):10.1111/jiec.70031
Research Points/Summary
In this study, we analyzed the relationship between low-speed transportation modes (walking, running, cycling, etc.) and environmental factors (temperature, barometric pressure, humidity, wind speed, precipitation, nighttime light, green space, etc.) in Tokyo using high-resolution human flow data and satellite data. In addition to empirical evidence of the impact of environmental factors on mobility, the use of XGBoost, SHAP, and GWPR presents a new framework for understanding mobility that goes beyond traditional regression analysis and recent machine learning studies.
The analysis revealed that environmental factors have spatially different effects on people's mobility, with higher temperatures leading to lower low-speed traffic in urban areas, while a positive correlation was observed in rural areas.
Background and Objectives
Low-speed transportation modes are closely related to the economy, vitality, and sustainable development of cities. As the effects of climate change intensify, it is becoming increasingly important to study the interactions between these modes of transportation and environmental factors in detail, but until now, not enough research has been done.
Previous studies have used indices that are updated less frequently than satellite data and OD (origin-destination) data, making it difficult to capture fine-scale changes in migration. This study aims to clarify the relationship between human flow data and satellite data and their spatial variability.
analysis
The study area was Tokyo, the spatial unit was 250 m mesh, and the temporal unit was monthly data. The period covered was 24 months, from January 2019 to December 2020, and the impact of COVID-19 was taken into account.
XGBoost was employed to build a highly accurate forecasting model, with a cross-validation accuracy of 88.29%. In addition, Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) were used to enhance the interpretability of the model, and Geographic Weighted Panel Regression (GWPR) was utilized to capture differences in geographic factors.
As environmental factors, we use weather data, such as temperature and precipitation, and also analyze sanitation-related data, such as
Night Light (NTL):Intensity of light at night from cities and settlements
NDVI (Normalized Vegetation Index):Indicators of the activity and amount of vegetation on the ground surface
PBLH (Planetary Boundary Layer Height):An indicator of the ease of diffusion of substances in the atmosphere. The higher the value, the easier it is to diffuse, and the lower the value, the easier it is to stay in the atmosphere.
result
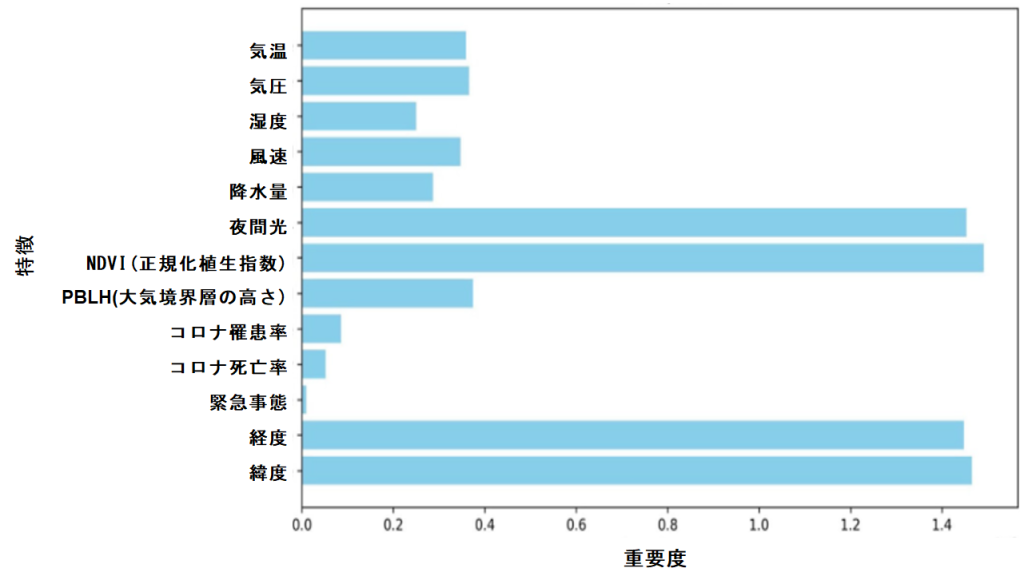
Figure 1 shows the importance of the explanatory variables, with NTL, NDVI, longitude, and latitude having the highest importance, temperature, barometric pressure, humidity, wind speed, precipitation, and PBLH having moderate importance, and COVID-19 related variables having the lowest importance.
Figure 2 shows the relationship between low-speed traffic and each environmental factor.
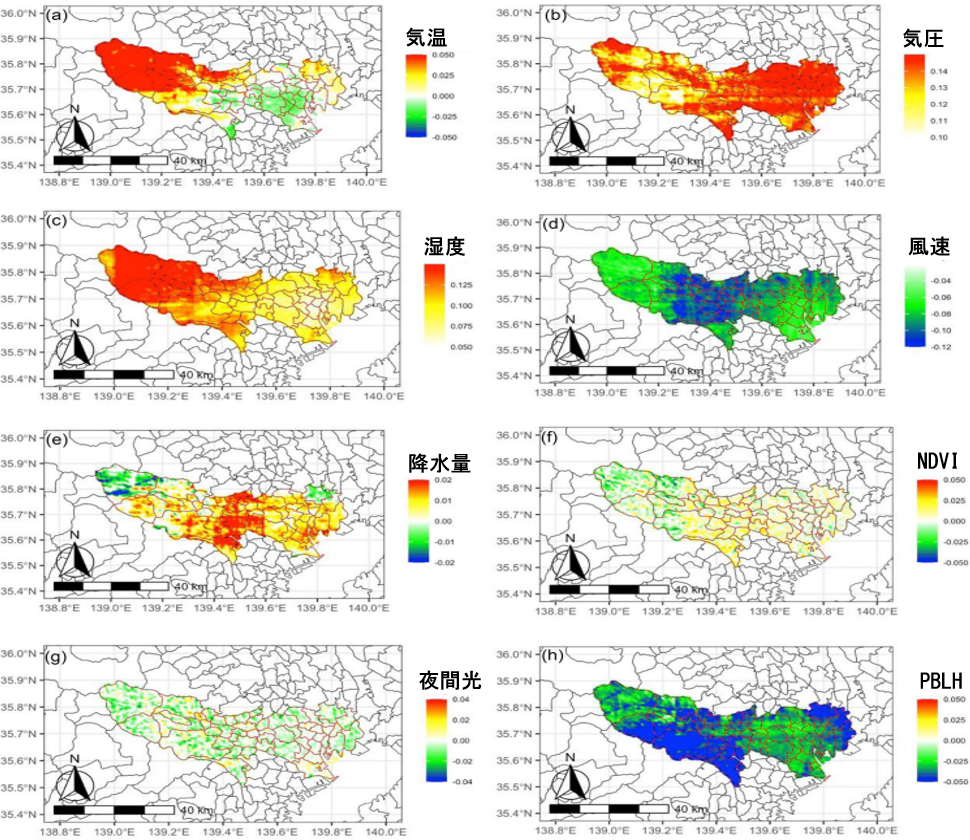
Red is more positively correlated, blue is more negatively correlated
consideration
Temperature, precipitation, NDVI, and nighttime light all showed significant spatial variation by location. In particular, an interesting duality was observed: higher temperatures lead to a decrease in low-speed traffic in urban areas, while increasing it in rural areas.
This may be because high temperatures in urban areas discourage walking, whereas in rural areas they encourage activity in the natural environment.
Relatively high humidity and precipitation may also increase human comfort and lead to increased walking and cycling.
Higher wind speeds reduced low-speed traffic, consistent with previous studies.
The mainly negative relationship between nighttime light and low-speed traffic may reflect a situation where there are fewer pedestrians on busy streets.
The relationship between green space and human mobility was spatially non-stationary, with negative effects found in hard-to-access locations and urban centers. This can be attributed to the scarcity of green spaces and the degree of urban development. In general, green space is considered a positive facilitator of human mobility.
COVID-19 had a negative impact on people's mobility.
The study suggests that investments in climate-adaptive infrastructure, such as cool pavement technology, increased tree cover, and pedestrian-oriented urban design, can be effective in promoting sustainable low-speed traffic.
summary
This study has shown that the development of the urban environment has a direct impact on people's mobility behavior, which in turn spills over into economic activity, health, and wellbeing. When incorporating new evaluation axes such as circular economy and wellbeing into ESG, it is important to have a quantitative perspective on such multidimensional causal relationships. aiESG Inc. provides a system that integrates the interrelationships among the environment, society, and the economy to realize data-based ESG evaluations.
About the services of aiESG, Inc:https://aiesg.co.jp/service/
















